# 138 Copy List with Random Pointer
A linked list is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer which could point to any node in the list or null.
Return a deep copy of the list.
Example 1:
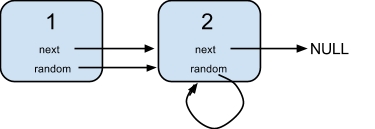
Input:
{"$id":"1","next":{"$id":"2","next":null,"random":{"$ref":"2"},"val":2},"random":{"$ref":"2"},"val":1}
Explanation:
Node 1's value is 1, both of its next and random pointer points to Node 2.
Node 2's value is 2, its next pointer points to null and its random pointer points to itself.Note:
You must return the copy of the given head as a reference to the cloned list.
這題是要複製一個linked list。
如 : head linked list
memory: 0x11 0x88
__
| |
r ↓
head ◇→→→ ◇→→→ null
r ↑
|______|
next: 0x88 null
random: 0x88 0x88
val: 1 2
原題目裡的輸入:
{"$id":"1","next":{"$id":"2","next":null,"random":{"$ref":"2"},"val":2},"random":{"$ref":"2"},"val":1}
我轉成如下:
{"$id":"1",
"next":
{"$id":"2",
"next":null,
"random":{"$ref":"2"},
"val":2},
"random":{"$ref":"2"},
"val":1}
你要回傳:
memory: 0xa8 0x93
__
| |
r ↓
newlist ◇→→→ ◇→→→ null
r ↑
|______|
next: 0x93 null
random: 0x93 0x93
val: 1 2
這裡可以有一個方式就是直接建一個新的,但因為原Node裡的random指的可能是下一個Node,或是下下個Node,這裡要注意的是,參考也是要指向新的Node。個人做法是先用一個while 迴圈把原來head linked list的next給new出來給新的n listed list。再用一個while迴圈處理random。但因random是某個next Node,但重點是要給他新linked list 的參考,而不是給head linded list 的參考。
程式碼:
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null){
return head;
}
Node t = new Node(head.val, null, null);
Node n = t;
Node h = head;
while(head != null){
Node ne = null;
if(head.next != null){
ne = new Node(head.next.val, head.next.next, null);
t.next = ne;
}
t = t.next;
head = head.next;
}
head = h;
t = n;
while(head != null){
if(head.random != null){
Node tempN = n;
while(n != null){
if(n.val == head.random.val){
t.random = n;
}
n = n.next;
}
n = tempN;
}
t = t.next;
head = head.next;
}
return n;
}
}這個做是正確的,但時間秏很多,因為每一個Noded的random會要重新遍尋整個n list。
該題還有另一個比省時間的做法,就是在原來的Node的下一個複製一個一樣的copy的Node。
分三次,第一次是在head linked list 的每一個Node的下一個COPY一個一樣val的Node
memory: 0x11 0x88
__
| |
r ↓
head ◇→→→ ◇→→→ null
r ↑
|______|
next: 0x88 null
random: 0x88 0x88
val: 1 2
while run one:
memory: 0x11 0x25 0x88
___
| |
r ↓
head ◇→→→ ◇→→→ ◇→→→ null
r ↑
|_____________|
next: 0x25 0x88 null
random: 0x88 null 0x88
val: 1 1 2
while run two:
memory: 0x11 0x25 0x88 0xb5
___
| |
r ↓
head ◇→→→ ◇→→→ ◇→→→ ◇→→→ null
r ↑
|_____________|
next: 0x25 0x88 0xb5 null
random: 0x88 null 0x88 null
val: 1 1 2 2
第二部分:將COPY的Node裡的random指向新的copy Node,也就是0x25 Node 及 0xb5的Node的random要指向新的COPY的Node 0xb5
memory: 0x11 0x25 0x88 0xb5
___
| |
r ↓
head ◇→→→ ◇→→→ ◇→→→ ◇→→→ null
r ↑
|_____________|
next: 0x25 0x88 0xb5 null
random: 0x88 null 0x88 null
val: 1 1 2 2
while run once:
memory: 0x11 0x25 0x88 0xb5
______________
| |
| ___ |
| | | |
r r ↓ ↓
head ◇→→→ ◇→→→ ◇→→→ ◇→→→ null
r ↑
|_____________|
next: 0x25 0x88 0xb5 null
random: 0x88 0xb5 0x88 null
val: 1 1 2 2
while run two:
memory: 0x11 0x25 0x88 0xb5
______________
| |
| ___ |
| | | |
r r ↓ ↓
head ◇→→→ ◇→→→ ◇→→→ ◇→→→ null
r ↑ r ↑
|_____________| |__|
next: 0x25 0x88 0xb5 null
random: 0x88 0xb5 0x88 0xb5
val: 1 1 2 2
第三部分,就是新的Node指向copy的Node,把原head Node指向原來head Node,並回傳新node 的next即可
memory: 0x11 0x25 0x88 0xb5
______________
| |
| ___ |
| | | |
r r ↓ ↓
head ◇→→→ ◇→→→ ◇→→→ ◇→→→ null
r ↑ r ↑
|_____________| |__|
next: 0x25 0x88 0xb5 null
random: 0x88 0xb5 0x88 0xb5
val: 1 1 2 2
while run once:
memory: 0x11 0x25 0x88 0xb5
___________________
| |
| ↑→→→→→→→→→→→↓ |
| ↑ ___ ↓ |
| ↑ | | ↓ |
r ↑ r ↓ ↓ ↓
head ◇→→↓ ◇→→→↑ ◇→→→ ◇→→→ null
r ↓ ↑ ↑ r ↑
| ↓→→→→→→→→→→→→↑ | | |
| | | |
|________________| |__|
next: 0x88 0xb5 0xb5 null
random: 0x88 0xb5 0x88 0xb5
val: 1 1 2 2
while run two:
memory: 0x11 0x25 0x88 0xb5
______________________________
| |
| ↑→→→→→→→→→→→→→→→→→→→→→→→↓ |
| ↑ ____ ↓ |
| ↑ | | ↓ |
r ↑ r ↓ ↓ ↓
head ◇→→↓ ◇→→→↑ ◇→→→null ◇→→→ null
r ↓ ↑ ↑ r ↑
| ↓→→→→→→→→→→→→↑ | | |
| | | |
|________________| |__|
next: 0x88 0xb5 null null
random: 0x88 0xb5 0x88 0xb5
val: 1 1 2 2因新的linked list 是Node dummyHead = new Node(); 所以回傳時,要回傳dummyHead.next才是
三部分是參考別人的方式程式碼如下: 我私自增加的print的部分來了解別人的程式碼。這個方式效率比我原來的好多!
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null){
return head;
}
//print
Node test = head;
while(test != null){
System.out.println("old.val = " +test.val + " , memory old " + test);
if(test.next != null){
System.out.println("old.next.val= " + test.next.val + " , memory old.next = " +test.next);
}else{
System.out.println("old.next.val==null ");
}
if(test.random != null){
System.out.println("old.random.val= " + test.random.val + " ,memory old.random = " + test.random );
if(test.random.next != null){
System.out.println(", old.random.next.val= " +test.random.next.val+ " ,memory old.random.next = " + test.random.next );
}
}
test= test.next;
System.out.println("\n");
}
//print
Node curr = head;
Node next;
// clone except for random pointers. Interweave alongside
while (curr != null) {
next = curr.next;
Node copy = new Node(curr.val, null, null);
curr.next = copy;
copy.next = next;
curr = next;
}
//print
test = head;
while(test != null){
System.out.println("test.val = " +test.val + " , memory test " + test);
if(test.next != null){
System.out.println("test.next.val= " + test.next.val + " , memory test.next = " +test.next);
}
if(test.random != null){
System.out.println("test.random.val= " + test.random.val + " ,memory test.random = " + test.random );
System.out.println(", test.random.next.val= " +test.random.next.val+ " ,memory test.random.next = " + test.random.next );
}
test= test.next;
System.out.println("\n");
}
// print
// link random
curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
if (curr.random != null){
System.out.println("curr.val = " +curr.val +", curr.random.val = " +curr.random.val);
if(curr.next!= null ){
System.out.println(" ,curr.next.val= " + curr.next.val);
if(curr.next.random != null){
System.out.println(" ,curr.next.random.val= " + curr.next.random.val);
}
}
if( curr.random.next != null){
System.out.println(" , curr.random.next.val = " +curr.random.next.val);
}
curr.next.random = curr.random.next;
}
curr = curr.next.next;
}
//print
test = head;
while(test != null){
System.out.println("2 test.val = " +test.val + " , memory test " + test);
if(test.next != null){
System.out.println("2 test.next.val= " + test.next.val + " , memory test.next = " +test.next);
}
if(test.random != null){
System.out.println("2 test.random.val= " + test.random.val + " ,memory test.random = " + test.random );
if(test.random.next != null){
System.out.println("2 , test.random.next.val= " +test.random.next.val+ " ,memory test.random.next = " + test.random.next );
}
}
test= test.next;
System.out.println("\n");
}
// print
// split list into original and clone
curr = head;
Node dummyHead = new Node();
Node cloneTail = dummyHead; // always points to tail of clone
Node cloneCurr;
while (curr != null) {
// save nodes before breaking links
next = curr.next.next; // orig's next
cloneCurr = curr.next; // clone's current
// extract clone list
cloneTail.next = cloneCurr;
cloneTail = cloneCurr;
// extract original
curr.next = next;
curr = next;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}看了別人的思路後,自已重寫一個一樣思路的。
程式碼:
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null){
return head;
}
//print
Node test = head;
while(test != null){
System.out.println("old.val = " +test.val + " , memory old " + test);
if(test.next != null){
System.out.println("old.next.val= " + test.next.val + " , memory old.next = " +test.next);
}else{
System.out.println("old.next.val==null ");
}
if(test.random != null){
System.out.println("old.random.val= " + test.random.val + " ,memory old.random = " + test.random );
if(test.random.next != null){
System.out.println(", old.random.next.val= " +test.random.next.val+ " ,memory old.random.next = " + test.random.next );
}
}
test= test.next;
System.out.println("\n");
}
//print
//original linked list ◇→◇→◇ ; new Linked list ◇→■→◇→■→◇→■ ==> new list ■→■→■
Node n = head;
Node t = null;
while(n != null){
t = n.next;
Node copy = new Node(n.val , null, null);
n.next = copy;
copy.next = t;
n= t;
}
n = head;
while(n != null){
if(n.random != null){
n.next.random = n.random.next;
}
n = n.next.next;
}
Node r = new Node();
Node rTail = r;
n = head;
while(n != null){
t = n.next.next;
rTail.next = n.next;
rTail = n.next;
//Next pointer of node with val 1 from the original list was modified.
//只有動到clone list是不行的,因為old 的list 的next 還是會指到新的list
//現在 ◇→■→◇→■→◇→■ ==> new list ◇ ◇ ◇
// ↘ ↘ ↘
// ■→→→ ■→→ ■→→ null
n.next = t;
//現在 ◇→■→◇→■→◇→■ ==> new list ◇ ◇ ◇
// ↘ ↘ ↘
// ■→→→ ■→→ ■→→ null
//現在 ◇→■→◇→■→◇→■ ==> new list ◇→→ ◇ ◇
// ↘ ↘
// ■→→→ ■→→ ■→→ null
//現在 ◇→■→◇→■→◇→■ ==> head list ◇→→ ◇→→ ◇→→ null
//
// rr □→→ ■→→→ ■→→ ■→→ null
n =t;
}
//print
Node rr = r;
while(r != null){
System.out.println("r.val = " + r.val+ " , memory r " + r);
if(r.next != null){
System.out.println("r.next.val= " + r.next.val + " , memory r.next = " +r.next);
}else{
System.out.println("r.next.val==null ");
}
if(r.random != null){
System.out.println("r.random.val= " + r.random.val + " ,memory r.random = " + r.random );
if(r.random.next != null){
System.out.println(",r.random.next.val= " +r.random.next.val+ " ,memory r.random.next = " + r.random.next );
}
}
System.out.println("\n");
r = r.next;
}
//print
return rr.next;
}
}去掉print版:
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null){
return head;
}
//original linked list ◇→◇→◇ ; new Linked list ◇→■→◇→■→◇→■ ==> new list ■→■→■
Node n = head;
Node t = null;
while(n != null){
t = n.next;
Node copy = new Node(n.val , null, null);
n.next = copy;
copy.next = t;
n= t;
}
n = head;
while(n != null){
if(n.random != null){
n.next.random = n.random.next;
}
n = n.next.next;
}
Node r = new Node();
Node rTail = r;
n = head;
// r = n.next;
// while(n != null){
// t = n.next;
// if(n.next != null){
// n.next = n.next.next;
// }else{
// n.next = null;
// }
// n =t;
// }
// this get Next pointer of node with val 1 from the original list was modified.
while(n != null){
t = n.next.next;
rTail.next = n.next;
rTail = n.next;
n.next = t;
n =t;
}
return rr.next;
}
}中間有注解的是產生「Next pointer of node with val 1 from the original list was modified.」因為Head的linked list的next Node指向新的linked list,這樣不行,所以要n.next = t; 才可以。
Last updated
Was this helpful?